Product Description
Water Ring Vacuum Pump / Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump (2BE4726)
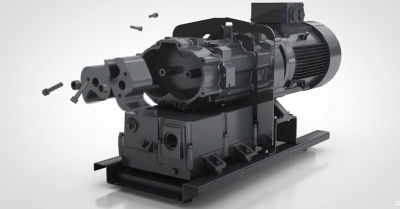
The 2BE4 vacuum pump produced by CHINAMFG International (Xihu (West Lake) Dis.) Co., Ltd was developed from the proven CHINAMFG 2BE3 pumps, whose reliable performance has been further improved..
The footprint and connections to the CHINAMFG 2BE4 models are identical to its predecessors, the CHINAMFG 2BE3 pump. Therefore, exchanging or upgrading to the more efficient CHINAMFG 2BE3 requires no site modifications.
The CHINAMFG 2BE4 model is available in cast iron, with stainless steel coming soon. The 2BE4 is perfect for use in mining, filter applications, paper mills, power plants, chemical plants, refineries and more
Main type for 2BE4 series vacuum pump and compressor
2BE4400,2BE4406,2BE4420,2BE4426,2BE4500,2BE4506,2BE4520,2BE4526,2BE4600,2BE4606, 2BE4620, 2BE4626, 2BE4 670, 2BE4676,2BE4 720,2BE4726
With our high products quality and good services, we have got the CE certificate for our products.
Our experienced and knowledgeable staff is dedicated to providing high quality products and after-sales supports.
Welcome clients from home and abroad to contact us and establish business relations
The main characteristics of 2BE4 series products:
All the bearings are the imported products with the brand name of CHINAMFG orNTN for ensuring the precise orientation and the high stability during the working of the pump.
The material of the impeller is QT400 nodular iron or stainless steel for ensuring the stability when the pump works under the rigorous condition and can extend the lifetime of the pump.
The casing is made of steel or stainless steel plates to extend the lifetime of the 2BE1 series pumps.
The shaft bushing is made of stainless steel to improve the lifetime of the pump 5 times than the normal material.
The V-belt pulley (when the pump is driven by the belt) is used the high precise pulley with taper bushing to keep the reliability of the pump and extend its life. And it is also easy to mantle and dismantle.
The coupling is used to drive the pump directly. The flexible part connecting the 2 half coupling is made of polyurethane that makes the pump more reliable.
The unique design to set the separator above the pump saves the space and decreases the noise efficiently.
All the parts are cast by the resin sands that make the pump surface very smooth. It is not necessary to cover the surface of the pumps with putty and gives out the heat efficiently.
The mechanical seals (optional) are used the imported products to avoid the leakage when the pump works for a long time.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Reciprocating Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Entrapment Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Vacuum Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Wet |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How Are Vacuum Pumps Employed in the Production of Electronic Components?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in the production of electronic components. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The production of electronic components often requires controlled environments with low or no atmospheric pressure. Vacuum pumps are employed in various stages of the production process to create and maintain these vacuum conditions. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps are used in the production of electronic components:
1. Deposition Processes: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in deposition processes, such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which are commonly employed for thin film deposition on electronic components. These processes involve the deposition of materials onto substrates in a vacuum chamber. Vacuum pumps help create and maintain the necessary vacuum conditions required for precise and controlled deposition of the thin films.
2. Etching and Cleaning: Etching and cleaning processes are essential in the fabrication of electronic components. Vacuum pumps are used to create a vacuum environment in etching and cleaning chambers, where reactive gases or plasmas are employed to remove unwanted materials or residues from the surfaces of the components. The vacuum pumps help evacuate the chamber and ensure the efficient removal of byproducts and waste gases.
3. Drying and Bake-out: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the drying and bake-out processes of electronic components. After wet processes, such as cleaning or wet etching, components need to be dried thoroughly. Vacuum pumps help create a vacuum environment that facilitates the removal of moisture or solvents from the components, ensuring their dryness before subsequent processing steps. Additionally, vacuum bake-out is employed to remove moisture or other contaminants trapped within the components’ materials or structures, enhancing their reliability and performance.
4. Encapsulation and Packaging: Vacuum pumps are involved in the encapsulation and packaging stages of electronic component production. These processes often require the use of vacuum-sealed packaging to protect the components from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, or oxidation. Vacuum pumps assist in evacuating the packaging materials, creating a vacuum-sealed environment that helps maintain the integrity and longevity of the electronic components.
5. Testing and Quality Control: Vacuum pumps are utilized in testing and quality control processes for electronic components. Some types of testing, such as hermeticity testing, require the creation of a vacuum environment for evaluating the sealing integrity of electronic packages. Vacuum pumps help evacuate the testing chambers, ensuring accurate and reliable test results.
6. Soldering and Brazing: Vacuum pumps play a role in soldering and brazing processes for joining electronic components and assemblies. Vacuum soldering is a technique used to achieve high-quality solder joints by removing air and reducing the risk of voids, flux residuals, or oxidation. Vacuum pumps assist in evacuating the soldering chambers, creating the required vacuum conditions for precise and reliable soldering or brazing.
7. Surface Treatment: Vacuum pumps are employed in surface treatment processes for electronic components. These processes include plasma cleaning, surface activation, or surface modification techniques. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum environment where plasma or reactive gases are used to treat the component surfaces, improving adhesion, promoting bonding, or altering surface properties.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may be used in electronic component production, depending on the specific process requirements. Commonly used vacuum pump technologies include rotary vane pumps, turbo pumps, cryogenic pumps, and dry pumps.
In summary, vacuum pumps are essential in the production of electronic components, facilitating deposition processes, etching and cleaning operations, drying and bake-out stages, encapsulation and packaging, testing and quality control, soldering and brazing, as well as surface treatment. They enable the creation and maintenance of controlled vacuum environments, ensuring precise and reliable manufacturing processes for electronic components.
What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to support a range of critical operations. Some of the key roles of vacuum pumps in pharmaceutical manufacturing include:
1. Drying and Evaporation: Vacuum pumps are employed in drying and evaporation processes within the pharmaceutical industry. They facilitate the removal of moisture or solvents from pharmaceutical products or intermediates. Vacuum drying chambers or evaporators utilize vacuum pumps to create low-pressure conditions, which lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate at lower temperatures. By applying vacuum, moisture or solvents can be efficiently removed from substances such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), granules, powders, or coatings, ensuring the desired product quality and stability.
2. Filtration and Filtrate Recovery: Vacuum pumps are used in filtration processes for the separation of solid-liquid mixtures. Vacuum filtration systems typically employ a filter medium, such as filter paper or membranes, to retain solids while allowing the liquid portion to pass through. By applying vacuum to the filtration apparatus, the liquid is drawn through the filter medium, leaving behind the solids. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient filtration, speeding up the process and improving product quality. Additionally, vacuum pumps can aid in filtrate recovery by collecting and transferring the filtrate for further processing or reuse.
3. Distillation and Purification: Vacuum pumps are essential in distillation and purification processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Distillation involves the separation of liquid mixtures based on their different boiling points. By creating a vacuum environment, vacuum pumps lower the boiling points of the components, allowing them to vaporize and separate more easily. This enables efficient separation and purification of pharmaceutical compounds, including the removal of impurities or the isolation of specific components. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various distillation setups, such as rotary evaporators or thin film evaporators, to achieve precise control over the distillation conditions.
4. Freeze Drying (Lyophilization): Vacuum pumps are integral to the freeze drying process, also known as lyophilization. Lyophilization is a dehydration technique that involves the removal of water or solvents from pharmaceutical products while preserving their structure and integrity. Vacuum pumps create a low-pressure environment in freeze drying chambers, allowing the frozen product to undergo sublimation. During sublimation, the frozen water or solvent directly transitions from the solid phase to the vapor phase, bypassing the liquid phase. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient and controlled sublimation, leading to the production of stable, shelf-stable pharmaceutical products with extended shelf life.
5. Tablet and Capsule Manufacturing: Vacuum pumps are utilized in tablet and capsule manufacturing processes. They are involved in the creation of vacuum within tablet presses or capsule filling machines. By applying vacuum, the air is removed from the die cavity or capsule cavity, allowing for the precise filling of powders or granules. Vacuum pumps contribute to the production of uniform and well-formed tablets or capsules by ensuring accurate dosing and minimizing air entrapment, which can affect the final product quality.
6. Sterilization and Decontamination: Vacuum pumps are employed in sterilization and decontamination processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Autoclaves and sterilizers utilize vacuum pumps to create a vacuum environment before introducing steam or chemical sterilants. By removing air or gases from the chamber, vacuum pumps assist in achieving effective sterilization or decontamination by enhancing the penetration and distribution of sterilants. Vacuum pumps also aid in the removal of sterilants and residues after the sterilization process is complete.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry screw pumps, or liquid ring pumps, may be utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing depending on the specific requirements of the process and the compatibility with pharmaceutical products.
In summary, vacuum pumps play a vital role in various stages of pharmaceutical manufacturing, including drying and evaporation, filtration and filtrate recovery, distillation and purification, freeze drying (lyophilization), tablet and capsule manufacturing, as well as sterilization and decontamination. By enabling efficient and controlled processes, vacuum pumps contribute to the production of high-quality pharmaceutical products, ensuring the desired characteristics, stability, and safety.

How Do You Choose the Right Size Vacuum Pump for a Specific Application?
Choosing the right size vacuum pump for a specific application involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Required Vacuum Level: The first consideration is the desired vacuum level for your application. Different applications have varying vacuum level requirements, ranging from low vacuum to high vacuum or even ultra-high vacuum. Determine the specific vacuum level needed, such as microns of mercury (mmHg) or pascals (Pa), and choose a vacuum pump capable of achieving and maintaining that level.
2. Pumping Speed: The pumping speed, also known as the displacement or flow rate, is the volume of gas a vacuum pump can remove from a system per unit of time. It is typically expressed in liters per second (L/s) or cubic feet per minute (CFM). Consider the required pumping speed for your application, which depends on factors such as the volume of the system, the gas load, and the desired evacuation time.
3. Gas Load and Composition: The type and composition of the gas or vapor being pumped play a significant role in selecting the right vacuum pump. Different pumps have varying capabilities and compatibilities with specific gases. Some pumps may be suitable for pumping only non-reactive gases, while others can handle corrosive gases or vapors. Consider the gas load and its potential impact on the pump’s performance and materials of construction.
4. Backing Pump Requirements: In some applications, a vacuum pump may require a backing pump to reach and maintain the desired vacuum level. A backing pump provides a rough vacuum, which is then further processed by the primary vacuum pump. Consider whether your application requires a backing pump and ensure compatibility and proper sizing between the primary pump and the backing pump.
5. System Leakage: Evaluate the potential leakage in your system. If your system has significant leakage, you may need a vacuum pump with a higher pumping speed to compensate for the continuous influx of gas. Additionally, consider the impact of leakage on the required vacuum level and the pump’s ability to maintain it.
6. Power Requirements and Operating Cost: Consider the power requirements of the vacuum pump and ensure that your facility can provide the necessary electrical supply. Additionally, assess the operating cost, including energy consumption and maintenance requirements, to choose a pump that aligns with your budget and operational considerations.
7. Size and Space Constraints: Take into account the physical size of the vacuum pump and whether it can fit within the available space in your facility. Consider factors such as pump dimensions, weight, and the need for any additional accessories or support equipment.
8. Manufacturer’s Recommendations and Expert Advice: Consult the manufacturer’s specifications, guidelines, and recommendations for selecting the right pump for your specific application. Additionally, seek expert advice from vacuum pump specialists or engineers who can provide insights based on their experience and knowledge.
By considering these factors and evaluating the specific requirements of your application, you can select the right size vacuum pump that meets the desired vacuum level, pumping speed, gas compatibility, and other essential criteria. Choosing the appropriate vacuum pump ensures efficient operation, optimal performance, and longevity for your application.


editor by CX 2024-04-17
Leave a Reply