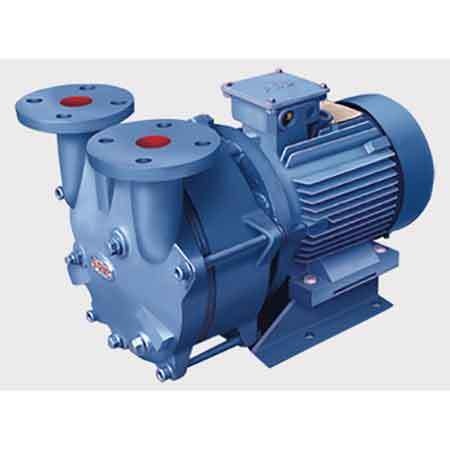
Product Description
Sanitary centrifugal pump is 1 type of centrifugal pump which mainly used for
pharmaceutical,food industry, dairy industy.
Sanitary (hygienic )centrifugal pump is 1 type of centrifugal pump which mainly used for pharmaceutical,
food industry,dairy industry, winery ,turnkey project .The pumps are made of Stainless steel 316L or SS 304 ,which with a surface polished ,can be used to the above industry for sanitary purpose
| Technical Parameters | |
| Flow Medium Parts | AISI304/AISI316L(1.4301/1.4404) |
| Without Flow Medium Parts | AISI304(1.4301) |
| Outside Surface | Semi bright |
| Inside Surface | Polished Ra0.4 |
| Product Wetted Seals | EPDM,Silicone,FPM.NBR |
| Max.Inlet Pressure | 0.5MPA |
| Temperature Range | -10ºC~140ºC |
| Noise Level(At 1m) | 60-80dB(A) |
| Capacity | 1.5~200ton/hour |
| Motor | ABB Motor and China motor,Siemens |
| Voltage | 220V,380V,440V,480V,ect |
| Impeller Type | Closed Impeller,Open Impeller,Semi-Open Type Impeller |
| Connection ends | Triclover,butt weld,threaded,union and flange |
| Machanical seal(standard) | plumbago&silicon carbide |
Technical Parameter
| Specification: | 3T-180T, 6m-60m, 0.55KW-75KW |
| Material: | SS304 SS316L (The pump body, pump cover and impeller) |
| Impeller: | 1.Open type impeller, there is no blind corner;2Close type impeller;3.Semi-open type impeller |
| Operate condition: | Sanitary centrifugal pump is close to HORIZONTAL transport of high and low level, is not the Self-priming type. |
| Surface treatment: | The part contact with mdedium is Polished, And other part is Sand Blasted |
| Max inlet pressure | 0.5MPa |
| Temperature range: | -10 to Degree +140 Degree |
| Flushable mechanical sealing: | Water pressure: __Max 0.1MPa Water lift: ___0.25-0.5L/min |
| Standards: | DIN \ SMS |
Motor
| 1. Configuration of “ABB” brand three-phase AC motor is in accordance with the International Electrotechnical CommissionIEC60034. IEC60072 standard design comply with European “CE” Marking requirements |
| 2. The Explosion-Proof motor also available, that can meet with the requirement of different Applications. |
| 3. It has excellent electric performance, low niose and low vibration. The protection grade is IP55, insulation grade is F. |
| 4. Operate involtage: 3Kw, 220-240V/380-420V 3Kw, 380-420V/660-690V |
| 5. Requency: 50Hz/60Hz |
| 6. Working method: Continuous(SI) |
| 7. Rotate speed: The standard rotate speed is 2900r/min |
1.Q:Why choose us ?
A: I.We only purchase top quality materiel in china, and our company also issued a strict rules for checking the quality, and all these points assure our best quality turbos.
II.The mould and equipment we used for production are of the best line in China.
III.The production craft and technology we adopted are the best in China also.
IV.Factories certified by ISO9001:2000 & ISO Quality Management Systems.
2.Q: Which shipment you can supply?
A: we ship cargo by sea, by air, by train or by express (FEDEX, DHL,UPS,TNT ). We make sure deliver goods by safe and economical methods and offer perfect package as you expect.
3. Q: what is your payment terms ?
A: our payment terms is T/T 30% deposit before production, 70% balance before delivery or against B/L copy
4. Q: What is your terms of delivery?
A: EXW ,FOB, CIF is available for us.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Max.Head: | 80-110m |
|---|---|
| Max.Capacity: | 50-100 L/min |
| Driving Type: | Motor |
| Impeller Number: | Single-Stage Pump |
| Working Pressure: | Middle Pressure Pump |
| Influent Type of Impeller: | Single Suction Pump |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
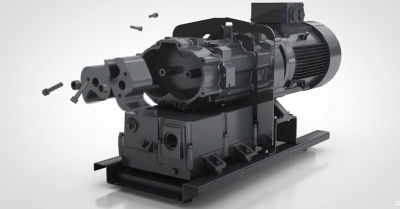
What Are the Advantages of Using Oil-Sealed Vacuum Pumps?
Oil-sealed vacuum pumps offer several advantages in various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. High Vacuum Performance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are known for their ability to achieve high levels of vacuum. They can create and maintain deep vacuum levels, making them suitable for applications that require a low-pressure environment. The use of oil as a sealing and lubricating medium helps in achieving efficient vacuum performance.
2. Wide Operating Range: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps have a wide operating range, allowing them to handle a broad spectrum of vacuum levels. They can operate effectively in both low-pressure and high-vacuum conditions, making them versatile for different applications across various industries.
3. Efficient and Reliable Operation: These pumps are known for their reliability and consistent performance. The oil-sealed design provides effective sealing, preventing air leakage and maintaining a stable vacuum level. They are designed to operate continuously for extended periods without significant performance degradation, making them suitable for continuous industrial processes.
4. Contamination Handling: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are effective in handling certain types of contaminants that may be present in the process gases or air being evacuated. The oil acts as a barrier, trapping and absorbing certain particulates, moisture, and chemical vapors, preventing them from reaching the pump mechanism. This helps protect the pump internals from potential damage and contributes to the longevity of the pump.
5. Thermal Stability: The presence of oil in these pumps helps in dissipating heat generated during operation, contributing to their thermal stability. The oil absorbs and carries away heat, preventing excessive temperature rise within the pump. This thermal stability allows for consistent performance even during prolonged operation and helps protect the pump from overheating.
6. Noise Reduction: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps generally operate at lower noise levels compared to other types of vacuum pumps. The oil acts as a noise-damping medium, reducing the noise generated by the moving parts and the interaction of gases within the pump. This makes them suitable for applications where noise reduction is desired, such as laboratory environments or noise-sensitive industrial settings.
7. Versatility: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are versatile and can handle a wide range of gases and vapors. They can effectively handle both condensable and non-condensable gases, making them suitable for diverse applications in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and research laboratories.
8. Cost-Effective: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are often considered cost-effective options for many applications. They generally have a lower initial cost compared to some other types of high-vacuum pumps. Additionally, the maintenance and operating costs are relatively lower, making them an economical choice for industries that require reliable vacuum performance.
9. Simplicity and Ease of Maintenance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are relatively simple in design and easy to maintain. Routine maintenance typically involves monitoring oil levels, changing the oil periodically, and inspecting and replacing worn-out parts as necessary. The simplicity of maintenance procedures contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness and ease of operation.
10. Compatibility with Other Equipment: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are compatible with various process equipment and systems. They can be easily integrated into existing setups or used in conjunction with other vacuum-related equipment, such as vacuum chambers, distillation systems, or industrial process equipment.
These advantages make oil-sealed vacuum pumps a popular choice in many industries where reliable, high-performance vacuum systems are required. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and consult with experts to determine the most suitable type of vacuum pump for a particular use case.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Chemical Distillation?
Yes, vacuum pumps are commonly used in chemical distillation processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Chemical distillation is a technique used to separate or purify components of a mixture based on their different boiling points. The process involves heating the mixture to evaporate the desired component and then condensing the vapor to collect the purified substance. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in chemical distillation by creating a reduced pressure environment, which lowers the boiling points of the components and enables distillation at lower temperatures.
Here are some key aspects of using vacuum pumps in chemical distillation:
1. Reduced Pressure: By creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment in the distillation apparatus, vacuum pumps lower the pressure inside the system. This reduction in pressure lowers the boiling points of the components, allowing distillation to occur at temperatures lower than their normal boiling points. This is particularly useful for heat-sensitive or high-boiling-point compounds that would decompose or become thermally degraded at higher temperatures.
2. Increased Boiling Point Separation: Vacuum distillation increases the separation between the boiling points of the components, making it easier to achieve a higher degree of purification. In regular atmospheric distillation, the boiling points of some components may overlap, leading to less effective separation. By operating under vacuum, the boiling points of the components are further apart, improving the selectivity and efficiency of the distillation process.
3. Energy Efficiency: Vacuum distillation can be more energy-efficient compared to distillation under atmospheric conditions. The reduced pressure lowers the required temperature for distillation, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs. This is particularly advantageous when dealing with large-scale distillation processes or when distilling heat-sensitive compounds that require careful temperature control.
4. Types of Vacuum Pumps: Different types of vacuum pumps can be used in chemical distillation depending on the specific requirements of the process. Some commonly used vacuum pump types include:
– Rotary Vane Pumps: Rotary vane pumps are widely used in chemical distillation due to their ability to achieve moderate vacuum levels and handle various gases. They work by using rotating vanes to create chambers that expand and contract, enabling the pumping of gas or vapor.
– Diaphragm Pumps: Diaphragm pumps are suitable for smaller-scale distillation processes. They use a flexible diaphragm that moves up and down to create a vacuum and compress the gas or vapor. Diaphragm pumps are often oil-free, making them suitable for applications where avoiding oil contamination is essential.
– Liquid Ring Pumps: Liquid ring pumps can handle more demanding distillation processes and corrosive gases. They rely on a rotating liquid ring to create a seal and compress the gas or vapor. Liquid ring pumps are commonly used in chemical and petrochemical industries.
– Dry Screw Pumps: Dry screw pumps are suitable for high-vacuum distillation processes. They use intermeshing screws to compress and transport gas or vapor. Dry screw pumps are known for their high pumping speeds, low noise levels, and oil-free operation.
Overall, vacuum pumps are integral to chemical distillation processes as they create the necessary reduced pressure environment that enables distillation at lower temperatures. By using vacuum pumps, it is possible to achieve better separation, improve energy efficiency, and handle heat-sensitive compounds effectively. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as the required vacuum level, the scale of the distillation process, and the nature of the compounds being distilled.

How Are Vacuum Pumps Different from Air Compressors?
Vacuum pumps and air compressors are both mechanical devices used to manipulate air and gas, but they serve opposite purposes. Here’s a detailed explanation of their differences:
1. Function:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps are designed to remove or reduce the pressure within a closed system, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. They extract air or gas from a chamber, creating suction or negative pressure.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors, on the other hand, are used to increase the pressure of air or gas. They take in ambient air or gas and compress it, resulting in higher pressure and a compacted volume of air or gas.
2. Pressure Range:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps are capable of generating pressures below atmospheric pressure or absolute zero pressure. The pressure range typically extends into the negative range, expressed in units such as torr or pascal.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors, on the contrary, operate in the positive pressure range. They increase the pressure above atmospheric pressure, typically measured in units like pounds per square inch (psi) or bar.
3. Applications:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps have various applications where the creation of a vacuum or low-pressure environment is required. They are used in processes such as vacuum distillation, vacuum drying, vacuum packaging, and vacuum filtration. They are also essential in scientific research, semiconductor manufacturing, medical suction devices, and many other industries.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors find applications where compressed air or gas at high pressure is needed. They are used in pneumatic tools, manufacturing processes, air conditioning systems, power generation, and inflating tires. Compressed air is versatile and can be employed in numerous industrial and commercial applications.
4. Design and Mechanism:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps are designed to create a vacuum by removing air or gas from a closed system. They may use mechanisms such as positive displacement, entrapment, or momentum transfer to achieve the desired vacuum level. Examples of vacuum pump types include rotary vane pumps, diaphragm pumps, and diffusion pumps.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors are engineered to compress air or gas, increasing its pressure and decreasing its volume. They use mechanisms like reciprocating pistons, rotary screws, or centrifugal force to compress the air or gas. Common types of air compressors include reciprocating compressors, rotary screw compressors, and centrifugal compressors.
5. Direction of Air/Gas Flow:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps draw air or gas into the pump and then expel it from the system, creating a vacuum within the chamber or system being evacuated.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors take in ambient air or gas and compress it, increasing its pressure and storing it in a tank or delivering it directly to the desired application.
While vacuum pumps and air compressors have different functions and operate under distinct pressure ranges, they are both vital in various industries and applications. Vacuum pumps create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment, while air compressors compress air or gas to higher pressures for different uses and processes.


editor by CX 2024-03-23
by
Leave a Reply